Versatile Industrial Application Adaptability
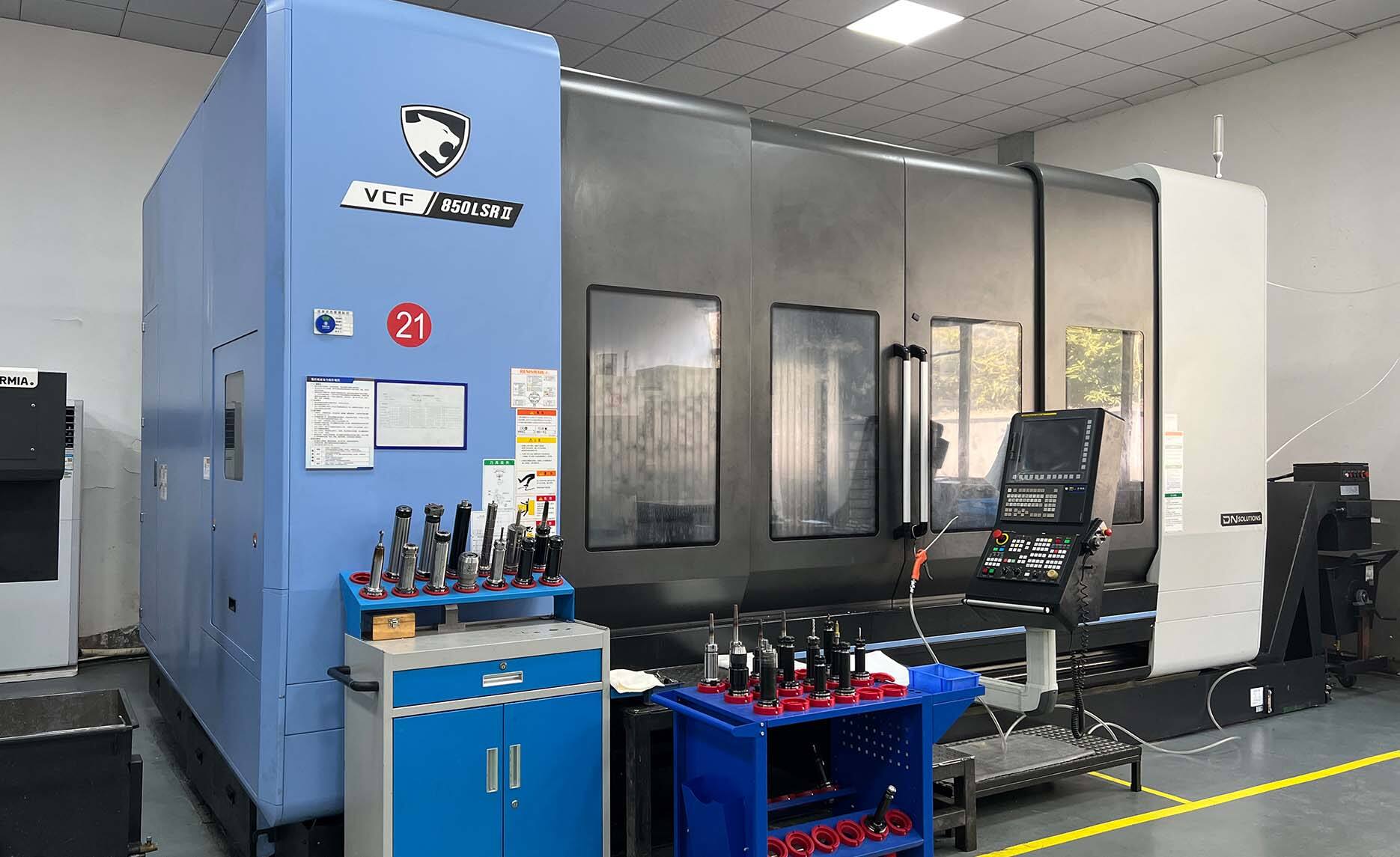
Annealing quenching and tempering demonstrates remarkable versatility across diverse industrial sectors, making it an indispensable process for modern manufacturing operations. The automotive industry extensively utilizes this treatment for engine components, transmission parts, suspension elements, and safety-critical components where reliability and performance are paramount. Gears, crankshafts, connecting rods, and valve springs all benefit from the enhanced properties achieved through annealing quenching and tempering, contributing to improved vehicle performance and longevity. In aerospace applications, the process enables the production of lightweight yet strong components that meet stringent safety and performance standards. Aircraft landing gear, engine components, and structural elements require the precise property control that annealing quenching and tempering provides. The construction equipment industry relies on this treatment for hydraulic components, cutting edges, wear plates, and structural elements that must withstand extreme operating conditions. The process adaptability allows for customization based on specific alloy compositions, enabling treatment of various steel grades, tool steels, and specialized alloys. Tool and die manufacturing sectors depend on annealing quenching and tempering to produce cutting tools, forming dies, and precision instruments with optimal hardness and wear resistance characteristics. The medical device industry utilizes the process for surgical instruments, implant components, and precision medical tools that require biocompatibility combined with mechanical excellence. Energy sector applications include turbine components, drilling equipment, and power generation machinery where reliability under extreme conditions is essential. The marine industry benefits from enhanced corrosion resistance and mechanical properties for propeller shafts, marine hardware, and offshore equipment. Agricultural equipment manufacturers use annealing quenching and tempering for tillage tools, harvesting equipment, and implement components that must withstand abrasive soil conditions. The process flexibility extends to batch sizes ranging from prototype quantities to high-volume production runs, making it economically viable for diverse manufacturing scales. Quality standards compliance across industries is facilitated by the consistent and predictable results achieved through properly controlled annealing quenching and tempering processes.